What Is a Motherboard?| Definition, Types, Components, and Functions
Introduction
In this article I am going to explain a very important topic, What is a Motherboard? This article also explains the key components and functions of a Motherboard, Types of Motherboards, History of Motherboard, etc. The Motherboard is the main component of a computer. It is often referred to as the main board or “mobo” for short. It is a large circuit board that fits into the computer case and it is where all the computer components connect to. A Motherboard is made of copper and fiberglass. Let’s define what is a motherboard.
What Is a Motherboard?

A motherboard is an electronic circuit board inside computing devices or computing systems such as personal computers, televisions, and monitors, as well as other expandable systems. The other common names of motherboards are mainboard, MB, Printed Circuit Board(PCB), main circuit board, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, mobo, etc. In Apple devices, it is called a logic board. The communication between different components of a system or computer such as the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and Memory is done with the help of a Motherboard or Mobo. Usually, a motherboard consists of some significant sub-systems like a Central Processor, interface connectors, memory controllers, etc. in short this board is referred to as the mother of all components attached to it.
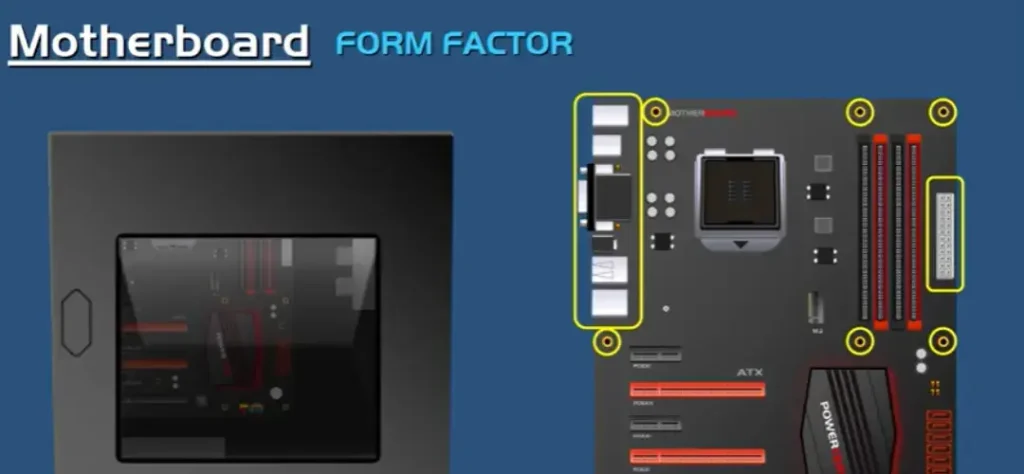
Form Factor
In computing, the form factor is the specification of a Motherboard, e.g the dimensions, Power Supply type, Location of Mounting Holes, Number of Ports on the Back Panel, etc. Specifically, in the IBM PC Compatible industry, standard form factors ensure that parts are interchangeable across competing genders and generations of technology, while in enterprise computing form factors ensure that server modules fit into existing rack mount systems.
History of Motherboard
The early computers were so large that they occupied a whole room. for processing, they had a cabinet instead of motherboards. Similarly, they had reel-to-reel tape drives, and flip switches instead of RAM and keyboards respectively. IBM used the first Motherboard in the early 1980s, named as Planar Breadboard designed by Engineer Petty McHugh.the key specifications of this board were a 4.7 megahertz Microprocessor,16 KB of Memory, 8-bit ISA Connector, etc. it is the main and crucial component of the computing devices or systems which supports the communication between other components and also connects all other peripherals.a computer is nothing without a motherboard.
How do motherboards work?
There is the CPU socket, where the CPU(Central Processing Unit) is placed. There are also the memory slots, where the Primary Memory DIMM Modules known as RAM are inserted, bus slots or expansion slots, and these are used to install various components to add more capabilities to a computer, such as a video card, sound card, network card and so on. Then there are also the SATA Connectors, and this is where you would attach your storage devices, such as SSDs, or Hard drives. Motherboard have several of these connectors so you can attach multiple storage drives. On some modern motherboards, you might find the M.2 slot, this is a newer slot for attaching an M.2 Solid State Drive. Also on modern motherboards, you will find the PCH or Platform Controller Hub. This hub is the latest chipset architecture by Intel that has replaced the older architecture.
Types of Motherboards
1-ATX(advanced technology extended) Motherboard

Motherboards come in different shapes and sizes, and this is known as a form factor. The most common motherboard form factor that is used in PCs today is ATX(advanced technology extended), it was created in 1995 and is now the de facto standard form factor for PCs today. A full-size ATX Motherboard is 12×9.6 inches.
2- Advanced Technology (AT) Motherboard

Now before the ATX was the AT(Advanced Technology) form factor, and this was used in the 1980s and was developed by IBM. Advanced Technology(AT) Motherboards are 12×13.8 inches in size and they are no longer in development since the succession of the ATX.
3-Micro ATX Motherboard
Another version of the ATX motherboard is the micro ATX. Micro ATX motherboards are smaller than ATX boards as its name suggests. Micro ATX boards are 9.6×9.6 inches. So it is a square design compared to the standard rectangular design of the ATX. These boards are cheaper than ATX boards and were designed to fit in smaller computer cases. They also have fewer features and consume less power than a standard ATX board.
4-Standard ATX motherboard
The dimensions of Standard ATX Motherboards are 305*244mm, and these dimensions are changed by different manufacturers. This kind of motherboard offers up to four expansion slots for RAM(Random Access Memory). It is an advanced version of AT Motherboard or Advanced Technology Motherboard and it was developed by Intel in the 1990s.
5-Flex ATX motherboard
these motherboards are known as compact family members of the ATX Motherboard family. they were designed to gain small space and they also had the lowest price tag. it is a modified version of the Mini ATX Motherboard by Intel between 1999 to 2000.
6-Low-Profile EXtended (LPX) motherboard

There were two major changes as compared to the older version of the motherboard, first, the riser card was added and second is output and input ports were moved to the device’s back. the addition of a riser card makes it simple to attach other components.
7-BTX motherboard

The abbreviation of BTX is Balanced Technology Extended and it was a strategy that was developed to meet the requirements of emerging technologies. It required more power consumption and as a result, it produced more heat. To focus on low-power consumption CPUs, Intel stopped the production of Balanced Technology Boards(BTX) Motherboards in the middle of the 2000s.
8-Pico BTX motherboard

As compared to the regular motherboard, the size of the Pico is smaller which is why it is called a Pico BTX Motherboard. it consists of two expansion slots and riser cards that help to fulfill the digital application needs.
9-Mini ITX motherboard

Mini ITX Motherboard ranges from 6.7×6.7 inches in dimensions. it is smaller than any other conventional motherboard. its small size and fan-less cooling enable it to have low power consumption. it can be used in any cases which are designed for ATX, Micro-ATX, and other ATX variants if needed.
10-Mini STX motherboard
Mini STX is commonly known as Mini Socket Technology Extended Motherboard, introduced by Intel in 2015. it ranges from 147mm by 147mm and is smaller than Mini ITX (170 mm x 170 mm).
Key Specifications of Mini STX motherboard
The key features and specifications of the Mini STX Motherboard may be changed as per the different manufacturer’s planning and designs as well. some common features are listed below.
Basic Key Components of a Motherboard
| Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Chipset | it is responsible for communication between the Central Processing Unit, Memory, and other peripherals as well. it also includes Northbridge and Southbridge chips. |
| CPU Socket | The place where the CPU is installed. it also supports different socket types. |
| Expansion Slots | These slots are used for graphics, sound, network, and other expansion cards. |
| RAM Slots | RAM Slots are responsible for holding RAM Modules and also support DDR types. |
| Power Connectors | These are the Connections for the power supply, which provides power to the motherboard and its other components. |
| SATA Connectors | Connectors for Serial ATA cables to connect storage devices such as hard drives and SSDs. |
| USB Headers | Ports for connecting USB devices like keyboards, mice, and external drives. |
| Motherboard Form Factor | Specification indicating the physical dimensions and layout of the motherboard. |
| Audio Connectors | Ports for audio input and output, including microphone and speaker jacks. |
| PCI or PCIe Power Connectors | Additional power connectors for high-performance graphics cards. |
| Cooling Connectors | |
| Ethernet Ports | Connector for a wired network connection. |
| CMOS Battery | Provides power to the CMOS memory, which stores BIOS settings. |
| BIOS/UEFI | Basic Input/Output System or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, firmware for system startup. |
Older motherboard components
On older motherboards there would be a couple of chips on the motherboard called a chipset. There would be the Northbridge Chip and the Southbridge Chip. and these chips would have different functions. The Northbridge, which was located on a Northern or upper portion of the motherboard acted like a middleman between the CPU, PCI Express bus, and memory. And the southbridge which was located on a southern or lower portion of the motherboard, was responsible for things like the standard PCI Slots, SATA connectors, USB ports, and so on. So for the CPU to communicate with these lower interfaces, it had to go through the southbridge. But now this architecture has been replaced by the platform controller hub chip.
Platform Controller Hub (PCH) Architecture
In the PCH architecture, the function of the northbridge has been largely integrated into the CPU so the northbridge chip has been eliminated and the functions of the southbridge are now done entirely by the platform controller hub chip. Now motherboards come with several input/output interfaces and these interfaces are largely located on the rear input/output panel of the motherboard. So for example, the most common interface on a motherboard is a USB-Universal Serial Bus port, and motherboards will typically have several USB ports because there are so many different peripherals that utilize the USB interface, such as keyboards, mice, cameras, external drives, and printers.
Functions of a Motherboard
Importance of Motherboard
The motherboard serves as a computer’s central hub. Hosting the CPU and RAM facilitates communication between important components. Expansion slots, USB ports, and audio jacks enable connectivity with peripherals, expanding functionality. Responsible for power distribution, it ensures all components receive necessary power. The BIOS/UEFI firmware initializes hardware during boot, providing foundational instructions for the operating system. The motherboard’s design and compatibility contribute to system stability. In short, it acts as the system’s backbone, orchestrating connections and determining overall functionality within a compact space.
FAQs on Motherboard
Where is the Motherboard located?
A computer motherboard may be found inside a computer casing, which is the point of connection for most of the computer’s elements and peripherals.
Why do motherboards need cooling?
Computer cooling is required to remove the waste heat produced by computer components, to keep components within permissible operating temperature limits.
What are the main functions of the motherboard?
The motherboard is the backbone that ties the computer’s components together at one spot and allows them to talk to each other. Without it, none of the computer pieces, such as the CPU, GPU, or hard drive, could interact.
Which company is best for motherboard?
MSI. MAG B660M Mortar WiFi DDR4 motherboard. …
Asus. Prime H610M-A D4. …
Gigabyte. B650E Aorus Master. …
ASRock. X670E Taichi. …
Asus. X570 ROG Crosshair VIII Hero Wi-Fi. …
Gigabyte. X570 I Aorus Pro Wi-Fi. View.
Asus. ROG Strix B550-F Gaming Wi-Fi. Check Price.
NZXT. N7 B550.
What is the most popular type of motherboard?
ATX
The most common motherboard form factor today is called ATX. Introduced by Intel Corp. in 1995 as an extension of the Baby AT form factor, ATX motherboards have a maximum size of 12 by 9.6 in. Smaller variants include the MiniATX, MicroATX and FlexATX.

